A number of sclerosis, an autoimmune illness that impacts 2.9 million individuals, presents a organic puzzle.
Many researchers suspect that the illness is triggered by a virus, often called Epstein-Barr, which causes the immune system to assault the nerves and might go away sufferers struggling to stroll or discuss. However the virus can’t be the entire story, since practically everyone seems to be contaminated with it in some unspecified time in the future in life.
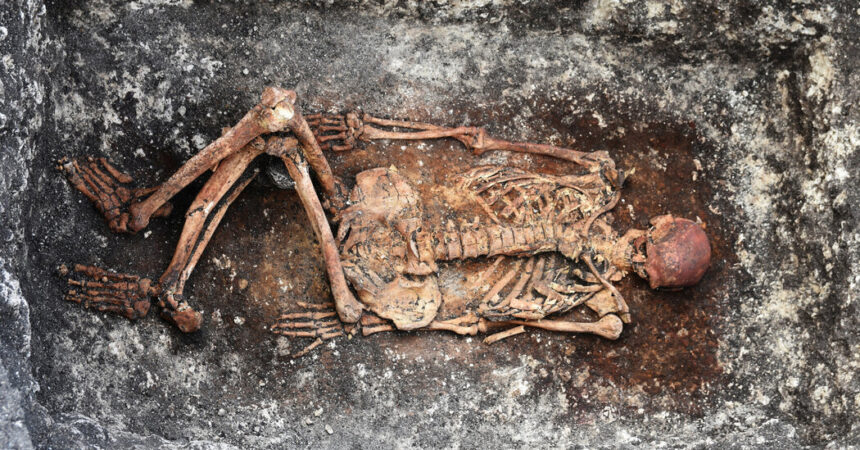
A brand new examine discovered a doable resolution to this paradox within the skeletal stays of a misplaced tribe of nomads who herded cattle throughout the steppes of western Asia 5,000 years in the past. It seems that the nomads carried genetic mutations that almost certainly protected them from pathogens carried by their animals, however that additionally made their immune methods extra delicate. These genes, the examine suggests, made the nomads’ descendants liable to a runaway immune response.
The discovering is an element of a bigger, unprecedented effort to know how the evolutionary previous has formed the well being of dwelling individuals. Researchers are analyzing hundreds of genomes of people that lived between Portugal and Siberia and between Norway and Iran roughly 3,000 to 11,000 years in the past. They hope to hint the genetic roots of not solely a number of sclerosis, but in addition diabetes, schizophrenia and plenty of different fashionable diseases.
“We’re taking historic human genomics to an entire new stage,” mentioned Eske Willerslev, a geneticist on the College of Copenhagen who led the hassle.
The researchers revealed the a number of sclerosis examine in addition to three different papers on the genetics and well being of historic peoples on Wednesday within the journal Nature.
For greater than a decade, Dr. Willerslev and different researchers have been pulling DNA from historic human bones. By evaluating the surviving genetic materials with that of dwelling individuals, the scientists have been capable of monitor a number of the most vital migrations of individuals internationally.
For instance, they’ve chronicled the motion of farmers from what’s now Turkey throughout Europe beginning about 8,000 years in the past. These early farmers encountered European hunter-gatherers who had lived on the continent for greater than 30,000 years. In some locations, hunter-gatherer DNA vanished from skeletons after the arrival of the farmers, suggesting violent conflicts. In different places, the 2 populations mingled sufficient to supply later generations with a blended ancestry.
Hundreds of years handed earlier than the following large migrational shift. About 5,000 years in the past, European DNA started to indicate the genetic signatures of a gaggle of pastoralists who lived on the steppes that stretch from Ukraine to Kazakhstan, referred to as the Yamnaya.
The Yamnaya traveled on horses and in wagons throughout a whole lot of miles of grassland, herding cows, goats and sheep alongside the best way. Even with out farms or cities, they prospered for hundreds of years, burying their useless with gold and jewellery.
Within the Bronze Age, the Yamnaya expanded their territory, sweeping by a lot of Asia in addition to Europe. Dr. Willerslev and his colleagues have discovered that when in Europe, the group typically worn out the farmers it encountered, though additionally they had peaceable relations in some locations.
At the moment, individuals in northern Europe can hint most of their ancestry to the Yamnaya. Farther south, Yamnaya ancestry is much less frequent. Individuals there as a substitute have extra ancestry from Close to East farmers and Europe’s earlier hunter-gatherers.
Dr. Willerslev and his colleagues puzzled what sort of genetic variations every historic group carried by every historic group and the way they affected their well being. To search out out, the researchers studied a few of their dwelling descendants.
They took benefit of UK Biobank, an enormous database of DNA and medical data. A lot of the 433,395 volunteers whom the scientists studied have been born in Britain, however 24,511 have been born in different international locations.
The researchers have been capable of tie hundreds of genetic variants within the database to elevated dangers for a variety of illnesses. They then in contrast the volunteers’ DNA with the genetic fragments from historic skeletons.
One evaluation discovered that hunter-gatherers from Western Europe, for instance, carried most of the variants that elevate the danger for prime ldl cholesterol, hypertension and diabetes. One other confirmed that historic Close to East farmers carried a excessive burden of variants linked to nervousness and different temper problems.
These findings don’t essentially imply that these historic individuals suffered from these circumstances. Genetic variants lay the lure, nevertheless it’s typically the atmosphere that springs it.
Diabetes, for instance, has grow to be more and more frequent within the fashionable world, partly due to a budget, sugar-loaded meals that makes up an rising a part of our weight-reduction plan. In earlier centuries, high-risk genes for diabetes could not have had the chance to offer rise to the illness.
In some circumstances, Dr. Willerslev and his colleagues discovered, these genetic variants offered historic peoples with a survival benefit.
The variants that elevate the danger of a number of sclerosis, for instance, grew to become steadily extra frequent among the many Yamnaya. The nomads who carried them seem to have had extra offspring than those that didn’t.
“These variants which are inflicting the excessive danger of a number of sclerosis right this moment should up to now have had a profit,” Dr. Willerslev mentioned.
The brand new research give some sturdy hints about what that profit is. Among the skeletons contained DNA not simply from people, but in addition from disease-causing viruses and micro organism. Many of those pathogens didn’t seem amongst hunter-gatherers and even among the many earliest farmers in Europe. However the Yamnaya stays contained the genetic signatures of quite a lot of pathogens, together with the one which precipitated plague.
“These variants appear to offer some type of safety from infectious illnesses,” Dr. Willerslev mentioned.
Plenty of research on a number of sclerosis counsel that the variants that elevate the danger of the illness additionally make the immune system’s assault towards viruses and micro organism extra aggressive.
Dr. Willerslev and his colleagues argued that the Yamnaya have been extra susceptible to animal illnesses than earlier people have been. The Yamnaya relied on animals for meat and milk and have been in fixed contact with their herds as they moved throughout the steppes.
These circumstances offered a brand new alternative for illnesses to leap to people. In response, the Yamnaya developed immune-related genes that helped them fend off the brand new enemies.
“They’ve made a extremely, actually compelling case,” Yassine Souilmi, a genomicist on the College of Adelaide in Australia, mentioned of Dr. Willerslev and his colleagues. “I’ll be shocked if additional experimental testing doesn’t match their conclusions.”
Dr. Lars Fugger, a a number of sclerosis skilled on the College of Oxford who collaborated with Dr. Willerslev on the brand new research, mentioned that the illness could not have grow to be frequent till current a long time. In right this moment’s atmosphere, with much less infectious illness than previous centuries, he mentioned, a robust immune system turns into extra prone to misfire, attacking its personal physique.
“Many people live in an atmosphere that’s squeaky clear,” Dr. Fugger mentioned. “The steadiness is now not there.”
Understanding the evolutionary roots of a number of sclerosis might information researchers to higher remedies for the illness. At the moment, the one efficient remedies for the situation are medication that suppress the immune system. To Dr. Fugger, these medication seem to be blunt devices towards a gently balanced a part of our biology.
“Reasonably than simply knocking it out, we should always simply attempt to discover out in better element the way it’s unbalanced, after which attempt to recalibrate it,” he mentioned.
The researchers are beginning comparable analyses of different illnesses, akin to schizophrenia and psoriasis. “That is just the start,” Dr. Fugger mentioned.
For now, they’re persevering with to depend on the UK Biobank, which suggests their outcomes might be largely restricted to genes which have influenced the well being of northern Europeans. “It could be phenomenal to have comparable research in different elements of the world,” mentioned Lluis Quintana-Murci, an evolutionary geneticist at Institut Pasteur who was not concerned within the analysis.
However there are few alternatives to hold out such research. Many international locations lack detailed digital well being data, for one factor. And unethical habits of Western scientists has left many Indigenous populations tired of donating DNA to such efforts.
Dr. Souilmi, who helps to construct a database for Indigenous Australians, mentioned that the totally different evolutionary path of every inhabitants might reveal vital insights about human biology on the whole. “By finding out different elements of the world, we’re truly broadening our understanding of all human circumstances right this moment,” he mentioned.