Throughout Kaspersky’s ninth annual Cyber Safety Weekend – META 2024 in Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, consultants delved into the altering cyberthreat panorama within the area.
The main target was on the safety challenges posed by rising applied sciences like Synthetic Intelligence (AI) and threats focusing on industrial management methods in crucial infrastructure throughout the Center East, Africa, and Asia. Kaspersky’s Cyber Immunity method was highlighted as a technique to develop options which are extremely immune to compromise, thereby minimizing potential vulnerabilities.
In Africa, Kaspersky’s telemetry revealed a 29% lower in general cyberthreats in South Africa in 2023 in comparison with 2022. Nevertheless, phishing assaults using social engineering techniques surged by 29%. In Kenya, general threats decreased by 8%, however ransomware assaults rose by 68%, whereas backdoors, exploits, and phishing elevated by 47%, 22%, and 19%, respectively. Nigeria skilled a ten% lower in general threats however witnessed an 8% improve in banking malware assaults geared toward stealing on-line banking credentials.
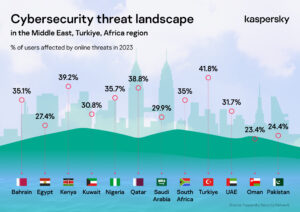
Evaluation by Kaspersky indicated fluctuations in on-line threats stemming from vulnerabilities on net pages, emails, or net companies throughout the area. The best variety of affected customers was noticed in Türkiye (41.8%), adopted by Kenya (39.2%), Qatar (38.8%), and South Africa (35%). Fewer customers had been affected in Oman (23.4%) and Egypt (27.4%), with Saudi Arabia (29.9%) and Kuwait (30.8%) falling in between.
Amin Hasbini, Director of META Analysis Middle International Analysis and Evaluation Group (GReAT) at Kaspersky, remarked on the evolving cybersecurity panorama and the rising range and class of cyber threats. He highlighted the position of superior applied sciences like AI and the geopolitical and financial turbulence within the META area, contributing to the rise in cybercrime and the complexity of cyberattacks.