What does a new child galaxy appear like?
For the longest time, many astrophysicists and cosmologists have assumed that new child galaxies would appear like the orbs and spidery discs acquainted within the fashionable universe.
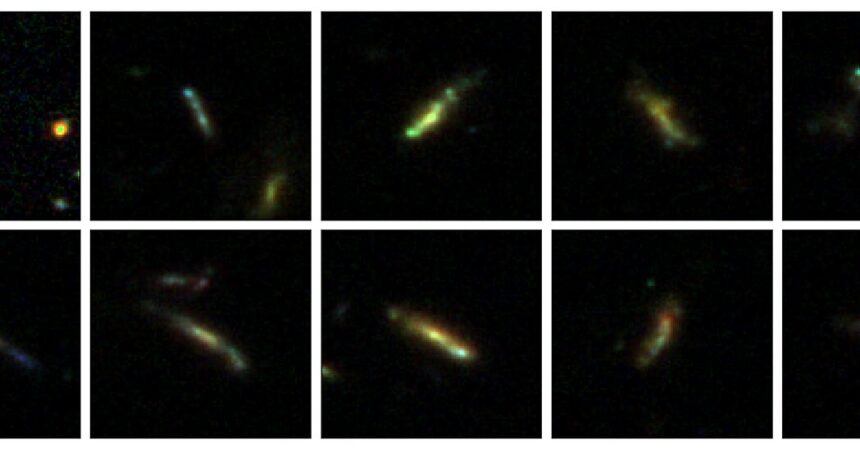
However in keeping with an evaluation of recent photos from the James Webb House Telescope, child galaxies had been neither eggs nor discs. They had been bananas. Or pickles, or cigars, or surfboards — select your personal metaphor. That’s the tentative conclusion of a staff of astronomers who re-examined photos of some 4,000 new child galaxies noticed by Webb on the daybreak of time.
“That is each a shocking and surprising end result, although there have been already hints of it with Hubble,” stated Viraj Pandya, a postdoctoral fellow at Columbia College, referring to the Hubble House Telescope. He’s the lead creator of a paper quickly to be printed within the Astrophysical Journal below the provocative title “Galaxies Going Bananas.” Dr. Pandya is scheduled to present a discuss his work on Wednesday at a gathering of the American Astronomical Society in New Orleans.
If the end result holds, astronomers say that it may profoundly alter their understanding of how galaxies emerge and develop. It may additionally provide perception into the mysterious nature of darkish matter, an unknown and invisible type of matter that astronomers say makes up a significant a part of the universe and outweighs atomic matter 5 to 1. Darkish matter engulfs galaxies and offers the gravitational nurseries during which new galaxies come up.
The end result builds on hints from earlier observations from the Hubble telescope that the earliest galaxies had been formed like pickles, stated Joel Primack, an astronomer on the College of California, Santa Cruz, and an creator of the brand new paper.
In an e-mail, Alan Dressler of the Carnegie Observatories, who was not a part of Dr. Pandya’s work, characterised the end result as “essential — I do suppose it can be crucial — extraordinarily essential, whether it is true.”
“I retain some skepticism about this end result, given how exhausting it’s to make such measurement,” he added. “Particularly for galaxies which are distant, small, and never very vibrant (I’m speaking in regards to the galaxies).”
Dr. Pandya’s staff analyzed the photographs of galaxies in a patch of sky smaller than a full moon often called the Prolonged Groth Strip, which has been surveyed by many different telescopes together with the Hubble telescope. The photographs had been obtained by a world collaboration referred to as the Cosmic Evolution Early Launch Science, or CEERS, survey.
The staff plans to increase its observations to different well-studied areas of the cosmos. “This may allow us to establish galaxies with completely different 3-D shapes everywhere in the sky” and facilitate much-needed spectroscopic follow-up observations, Dr. Pandya wrote in an e-mail.
Galaxies are the town states of the cosmos. Throughout the seen universe are an estimated two trillion of them, every containing as many as a trillion stars. However the seen universe is just a fraction of what’s on the market. A lot of the matter within the cosmos appears to be within the type of darkish matter; no matter darkish matter is, it constitutes the invisible bones of the universe we see.
Astronomers now suppose that galaxies had been seeded by random fluctuations within the density of matter and vitality through the Large Bang. As house expanded, the denser areas lagged and darkish matter pooled, pulling regular matter with it. This materials ultimately fell again collectively and lit up as stars and galaxies or disappeared into black holes. The Webb telescope was designed to analyze this formative and mysterious period; with an enormous mirror and infrared sensors, it might see probably the most distant, and thus earliest, galaxies.
Dr. Pandya and his collaborators investigated the three-dimensional shapes of galaxies by statistically analyzing their two-dimensional projections on the sky. If these early galaxies had been balls or disks randomly oriented in house, they need to often current their full faces, showing spherical and round, to telescopes.
However astronomers aren’t seeing a lot of that. As an alternative they see a lot of cigars and bananas.
“They persistently look very linear,” Dr. Pandya stated, “with some galaxies displaying a number of vibrant clumps organized like pearls on a necklace.”
Such rectangular galaxies are uncommon right this moment, however they make up as a lot as 80 p.c of the galaxies within the CEERS pattern, which reaches again to about 500 million years after the Large Bang.
“Their plenty are such that they might be the progenitors of galaxies just like the Milky Manner,” Dr. Pandya stated, “implying that our personal galaxy might have gone via an analogous cigar/surfboard morphological section prior to now.”
Within the fashionable universe galaxies appear to return in two primary kinds: featureless, roundish clouds referred to as ellipticals, and flat, spidery discs like our Milky Manner residence.
Evidently the earliest newborns didn’t begin out like that. The rationale, astronomers suspect, is said to the properties of darkish matter, however precisely which or how is unclear.
The main concept holds that darkish matter consists of clouds of unique subatomic particles left over from the Large Bang. Abnormal matter, drawn by gravity into these clouds, would condense and light-weight up into stars and galaxies, in keeping with laptop simulations.
In a well-liked variant referred to as chilly darkish matter, these leftover particles could be heavy and gradual in contrast with protons, neutrons and the opposite, extra acquainted denizens of the quantum atomic world. In response to laptop simulations, chilly darkish matter would clump simply to type the large-scale patterns astronomers see within the sky.
Figuring out these gradual, heavy particles would shake the world of particle physics and cosmology. However to date experiments in labs just like the Giant Hadron Collider at CERN have didn’t detect or produce any particles of chilly darkish matter. Currently, curiosity has shifted to different proposed types of darkish matter, together with an entire gallery — a “darkish sector” — of “darkish” particles interacting with each other invisibly via “darkish” forces.
On this combine are axions, which in concept are extraordinarily gentle and act extra like waves than particles — “fuzzy darkish matter,” or “wavy darkish matter,” within the vernacular. In laptop simulations of galaxy formation, such waves can intervene with each other, producing knobby filamentary buildings as a substitute of the spherical shapes predicted by chilly darkish matter.
“Sure, the darkish matter connection is tantalizing,” Dr. Pandya stated, including that the satan was within the messy particulars of “gastrophysics,” which describes how turbulence, scorching fuel and magnetic fields work together to gentle up stars and galaxies.
Jeremiah Ostriker, an emeritus professor of astrophysics at Princeton now affiliated with Columbia College, in recent times has turned his consideration to fuzzy darkish matter. In 1973, Dr. Ostriker conceived the concept of darkish matter along with his Princeton colleague James Peebles.
He and others have identified that fuzzy darkish matter would depart its personal signature on the dimensions and shapes of child galaxies. Due to their inherent waviness, axions wouldn’t clump as successfully as chilly darkish matter, so it will be exhausting for them to supply child galaxies of lower than one billion photo voltaic plenty. Chilly darkish matter has no such limitation. Right now’s telescopes are removed from delicate sufficient to watch such infants, nonetheless; a brand new era of even larger devices could also be wanted to complete the job.
When Dr. Ostriker discovered of Dr. Pandya’s work, he remarked that the prospects for fuzzy darkish matter had been wanting higher and higher. “Sustain the nice work.” he stated.