What number of methods are there to go away this universe?
Maybe the most effective identified exit entails the loss of life of a star. In 1939 the physicist J. Robert Oppenheimer and his scholar Harlan Snyder, of the College of California, Berkeley, predicted that when a sufficiently large star runs out of thermonuclear gasoline, collapses inward and retains collapsing without end, shrink-wrapping house, time and lightweight round itself in what at the moment is known as a black gap.
But it surely seems {that a} lifeless star may not be wanted to make a black gap. As an alternative, at the least within the early universe, large clouds of primordial gasoline could have collapsed straight into black holes, bypassing hundreds of thousands of years spent in stardom.
That’s the tentative conclusion just lately reached by a gaggle of astronomers learning UHZ-1, a speck of sunshine relationship from not lengthy after the Huge Bang. The truth is, UHZ-1 is (or was) a robust quasar that spat fireplace and X-rays from a monstrous black gap 13.2 billion years in the past, when the universe was not fairly 500 million years younger.
That’s unusually quickly, cosmically talking, for thus large a black gap to have come into being via stellar collapses and mergers. Priyamvada Natarajan, an astronomer at Yale and the lead writer of a paper revealed within the Astrophysical Journal Letters, and her colleagues, contend that in UHZ-1 they’ve found a brand new celestial species, which they name an overmassive black gap galaxy, or O.B.G. In essence, an O.B.G. is a younger galaxy anchored by a black gap that grew to become too large too quick.
The invention of this precocious quasar may assist astronomers clear up a associated puzzle that has tantalized them for many years. Practically each galaxy seen within the fashionable universe appears to harbor at its middle a supermassive black gap hundreds of thousands of billions of occasions as large because the solar. The place did these monsters come from? May abnormal black holes have grown so massive so quick?
Dr. Natarajan and her colleagues suggest that UHZ-1, and so maybe many supermassive black holes, started as primordial clouds. These clouds may have collapsed into kernels that had been precociously heavy — and had been ample to jump-start the expansion of overmassive black gap galaxies. They’re one other reminder that the universe we see is ruled by the invisible geometry of darkness.
“As the primary O.B.G. candidate, UHZ-1 supplies compelling proof for the formation of heavy preliminary seeds from direct collapse within the early universe,” Dr. Natarajan and her colleagues wrote. In an electronic mail, she added: “Nature does appear to make BH seeds some ways, past simply stellar loss of life!”
Daniel Holz, a theorist on the College of Chicago who research black holes mentioned: “Priya has discovered a particularly thrilling black gap, if true.”
He added, “It is just too large too early. It’s like wanting in at a kindergarten classroom and there amongst all of the 5-year-olds is one that’s 150 kilos and/or six ft tall.”
In response to the story that astronomers have been telling themselves in regards to the evolution of the universe, the primary stars condensed out of clouds of hydrogen and helium left over from the Huge Bang. They burned sizzling and quick, rapidly exploding and collapsing into black holes 10 to 100 occasions as large because the solar.
Over eons, successive generations of stars had been fashioned from the ashes of earlier stars, enriching the chemistry of the cosmos. And the black holes left over from their deaths stored merging and rising by some means, into the supermassive black holes on the facilities of galaxies.
The James Webb Area Telescope, launched two years in the past this Christmas, was designed to check this concept. It possesses the largest mirror in house, 21 ft in diameter. Extra vital, it was designed to document infrared wavelengths from the sunshine of probably the most distant and due to this fact earliest stars within the universe.
However as quickly as the brand new telescope was educated on the sky, it caught sight of latest galaxies so large and vivid that they defied cosmologists’ expectations. Arguments have raged for the final couple of years about whether or not these observations in reality threaten a longstanding mannequin of the cosmos. The mannequin describes the universe as composed of a hint of seen matter, astounding quantities of “darkish matter,” which supplies the gravity to carry galaxies collectively, and “darkish power,” pushing these galaxies aside.
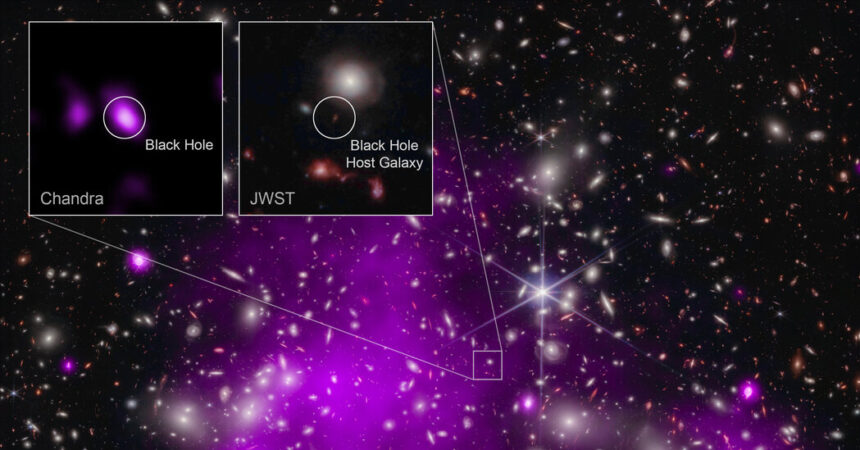
The invention of UHZ-1 represents an inflection level in these debates. In preparation for a future statement by the James Webb Area Telescope of an enormous cluster of galaxies within the constellation Sculptor, Dr. Natarajan’s crew requested for time on NASA’s Chandra X-ray Observatory. The cluster’s mass acts as a gravitational lens, magnifying objects far behind it in house and time. The researchers hoped to get a glimpse in X-rays of regardless of the lens may carry into view.
What they discovered was a quasar powered by a supermassive black gap about 40 million occasions as large because the solar. Additional observations by the Webb telescope confirmed that it was 13.2 billion light-years away. (The Sculptor cluster is about 3.5 billion light-years away.) It was probably the most distant and earliest quasar but discovered within the universe.
“We wanted Webb to search out this remarkably distant galaxy, and Chandra to search out its supermassive black gap,” Akos Bogdan of the Middle for Astrophysics Harvard & Smithsonian mentioned in a information launch. “We additionally took benefit of a cosmic magnifying glass that boosted the quantity of sunshine we detected.”
The outcomes point out that supermassive black holes existed as early as 470 million years after the Huge Bang. That isn’t sufficient time to permit the black holes created by the primary technology of stars — beginning out at 10 to 100 photo voltaic lots — to develop so large.
Was there one other solution to make even greater black holes? In 2017 Dr. Natarajan advised that collapsing clouds of primordial gasoline may have birthed black holes greater than 10,000 occasions as large because the solar.
“You may then think about one among these subsequently rising into this younger, precociously massive black gap,” Dr. Holz mentioned. Consequently, he famous, “at each subsequent time within the universe’s historical past there’ll at all times be some surprisingly massive black holes.”
Dr. Natarajan mentioned, “The truth that these begin out in life overmassive implies that they are going to probably ultimately evolve into supermassive black holes.” However nobody is aware of how that works. Black holes make up 10 % of the mass within the early quasar UHZ-1, whereas they compose lower than one one-thousandth of a % of the mass of modern-day galaxies like the large Messier 87, whose black gap weighed in at 6.5 billion photo voltaic lots when its image was taken by the Occasion Horizon Telescope in 2019.
That implies that difficult environmental suggestions results dominate the expansion and evolution of those galaxies and their black holes, inflicting their mass in stars and gasoline to bulk up.
“So in impact these extraordinarily early O.B.G.s are actually telegraphing far more details about, and illuminating, seeding physics moderately than later development and evolution,” Dr. Natarajan mentioned. She added: “Although they’ve vital implications.”.
Dr. Holz mentioned, “It might actually be cool if it seems to be what’s taking place, however I’m genuinely agnostic.” He added, “It’s going to be an interesting story irrespective of how we clear up the thriller of early large black holes.”