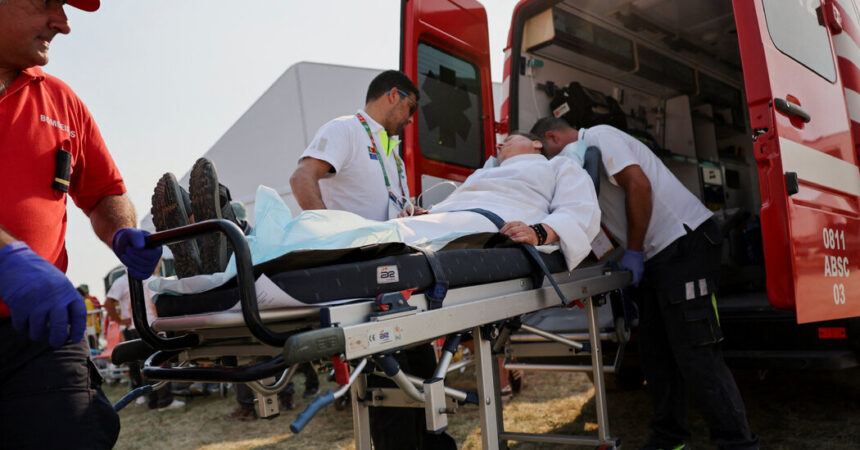
Local weather change continues to have a worsening impact on well being and mortality world wide, in line with an exhaustive report revealed on Tuesday by a global staff of 114 researchers.
One of many starkest findings is that heat-related deaths of individuals older than 65 have elevated by 85 % for the reason that Nineteen Nineties, in line with modeling that comes with each altering temperatures and demographics. Folks on this age group, together with infants, are particularly susceptible to well being dangers like warmth stroke. As world temperatures have risen, older individuals and infants now are uncovered to twice the variety of heat-wave days yearly as they had been from 1986 to 2005.
The report, revealed within the medical journal The Lancet, additionally tracked estimated misplaced revenue and meals insecurity. Globally, publicity to excessive warmth, and ensuing losses in productiveness or incapacity to work, could have led to revenue losses as excessive as $863 billion in 2022. And, in 2021, an estimated 127 million extra individuals skilled reasonable or extreme meals insecurity linked to warmth waves and droughts, in contrast with 1981-2010.
“We’ve misplaced very valuable years of local weather motion and that has come at an infinite well being price,” mentioned Marina Romanello, a researcher at College Faculty London and the manager director of the report, generally known as The Lancet Countdown. “The lack of life, the influence that folks expertise, is irreversible.”
The symptoms of public well being tracked within the report have usually declined over the 9 years the researchers have produced editions of the evaluation.
The evaluation additionally examined well being outcomes for particular person nations, together with america. Warmth-related deaths of adults 65 and older elevated by 88 % between 2018 and 2022, in contrast with 2000-04. An estimated 23,200 older Individuals died in 2022 due to publicity to excessive warmth.
For well being practitioners, the statistics usually are not summary or faceless.
“These numbers remind me of the aged sufferers I see in my very own hospital with heatstroke,” mentioned Dr. Renee Salas, an emergency medication doctor at Massachusetts Common Hospital and Harvard Medical College.
Dr. Salas is among the report’s co-authors and mentioned she seen the challenge like monitoring very important indicators in a affected person, however on a nationwide and worldwide scale.
The information may also help fill a niche for federal policymakers.
“We now have a restricted set of indicators for local weather change and well being which might be routinely collected in america,” mentioned Dr. John Balbus, director of the workplace of local weather change and well being fairness within the U.S. Division of Well being and Human Providers. He didn’t contribute to this report and isn’t at present concerned with The Lancet Countdown, however beforehand served as a scientific adviser to the challenge’s funder.
Dr. Balbus cautioned that this report principally measures individuals’s publicity to climate-related dangers moderately than precise well being outcomes, resembling charges of illness. So as to get from exposures to actual well being outcomes, he mentioned extra funding in analysis was wanted.
For the primary time, this yr’s Lancet Countdown included projections for the long run. If the worldwide common temperature rises by 2 levels Celsius in contrast with pre-industrial temperatures, an more and more doubtless future until society considerably reduces greenhouse fuel emissions, the variety of heat-related deaths every year will enhance by 370 % by the center of this century, the report discovered.
On the similar time, the researchers level out that lowering fossil gasoline air pollution is proving helpful for world well being. Deaths from air air pollution associated to fossil fuels have decreased by 15 % since 2005, with most of that enchancment a results of much less coal-related air pollution getting into the ambiance.
The worth of The Lancet Countdown is its ongoing monitoring of local weather change’s results on world well being, mentioned Sharon Friel, director of the Planetary Well being Fairness Hothouse on the Australian Nationwide College.
Dr. Friel was not concerned within the report, however learn it and wrote an accompanying commentary.
Dr. Howard Frumkin, a former particular assistant to the director for local weather change and well being on the Facilities for Illness Management and Prevention, mentioned the report was a useful dashboard however that the local weather impacts he most nervous about weren’t the apparent ones highlighted. Researchers and policymakers want to concentrate to the well being results of individuals being displaced by local weather change and migrating, Dr. Frumkin mentioned.
“For those who’re on most cancers chemotherapy or if you’re getting kidney dialysis or should you’re getting dependancy remedy and you need to transfer all of the sudden, that’s terribly disruptive and threatening,” he mentioned. Dr. Frumkin was not concerned within the new report however was a co-author on earlier editions.
Through the years, the well being consultants concerned on this challenge have included extra analysis in regards to the continued use of fossil fuels being the basis explanation for well being points.
“The analysis on this report may be very clear,” Dr. Salas mentioned. “Additional growth of fossil fuels is reckless and the info clearly exhibits that it threatens the well being and well-being of each individual.”
The researchers level out that well being care methods, and different societal infrastructure well being care will depend on, haven’t tailored shortly sufficient to our present stage of world warming.
“If we haven’t been in a position to cope at this time, likelihood is we gained’t have the ability to cope sooner or later,” Dr. Romanello mentioned.
The report is more likely to be mentioned on the annual United Nations local weather summit within the United Arab Emirates that begins in a number of weeks. This yr the summit will embrace a better concentrate on human well being.