Shallow waters, meet Christmas procuring.
Drought, aggravated by the burning of fossil fuels, is slowing down the ship site visitors that carries items out and in of the USA by way of the slender and important Panama Canal, whereas warmth and drought within the Midwest are threatening to dry out the Mississippi River, a vital artery for American corn and wheat exports, within the months forward.
It could possibly be worse. There could possibly be a number of droughts affecting a number of commerce routes on the identical time, disturbing the transport (and subsequent costs) of many kinds of items like liquefied pure gasoline and occasional beans. That may be a looming threat in a world that has grow to be accustomed to every little thing in every single place in any respect seasons.
Final 12 months, as an illustration, as Europe confronted its worst dry spell in 500 years, ships carried a fraction of the cargo they usually do alongside the Rhine in Germany, one of many continent’s most essential thoroughfares. The Rhine’s water ranges are higher this 12 months, however the river faces a longer-term local weather threat: The mountain snow and ice that feeds the Rhine is declining.
Exceptionally sizzling, dry circumstances throughout the center of the nation this summer season signifies that may occur once more this fall. That’s unhealthy information for American agriculture. Grains, grown within the Midwest, make their method down the Mississippi River by barge earlier than being shipped by way of the Panama Canal after which transported throughout the ocean.
“In September, we might have some compounding points,” mentioned Jon Davis, a meteorologist who works with Everstream Analytics, a personal firm that advises different organizations on local weather hazards in provide chains.
Drought is a recurrent pure phenomenon. Nevertheless, the dangers of drought are considerably increased in a world the place the typical world temperature is increased due to the burning of fossil fuels, coupled with the return of El Niño, a pure climate phenomenon that may final a number of years.
That would imply increased costs for American and European customers, or much less stuff on the cabinets, as retailers put together for vacation procuring.
“These sorts of points, general, have gotten extra frequent,” Mr. Davis added. “Dryness in Panama, low ranges within the Mississippi. Low ranges within the Rhine. That’s of concern to anybody that has pursuits in world commerce.”
Droughts should not the one threat to world provide chains. Abnormally sizzling ocean waters are supersizing storms. The Atlantic hurricane season has been extra energetic than ordinary; 9 named storms have been recorded by way of mid-August.
Ocean transport is how 90 p.c of world items attain one a part of the world from one other.
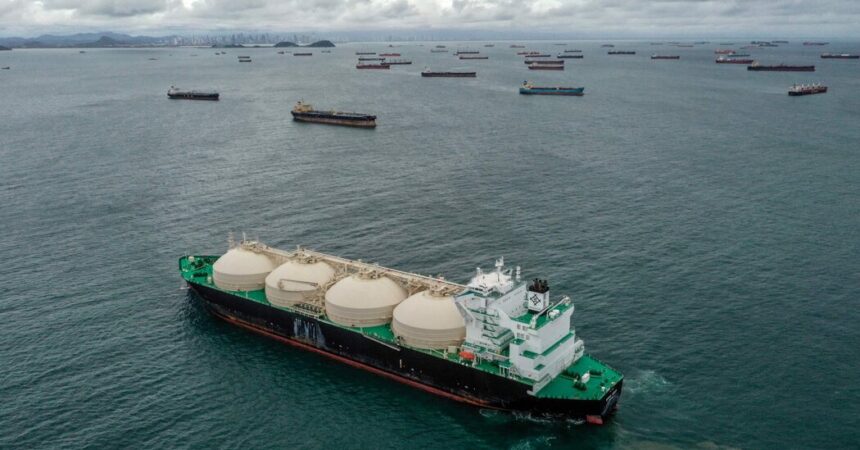
The realm across the Panama Canal is experiencing an exceptionally dry 12 months. That’s unhealthy for the canal, as a result of each ship that goes by way of wants tens of millions of gallons of freshwater to drift on, relying on what number of containers it’s carrying and the way heavy it’s.
Ships have needed to watch their weight this 12 months, which suggests decreasing cargo volumes. Fewer ships are going by way of every day; the Panama Canal Authority, which runs the waterway, has restricted the quantity to 32 per day now, in contrast with 36 to 38 at different factors.
There’s little rain within the forecast, which suggests the canal’s issues should not anticipated to ease up anytime quickly.
International commerce can be a part of the local weather drawback. Ships use heavy gasoline oil, which accounts for roughly 3 p.c of world greenhouse gasoline emissions. The trade not too long ago agreed to neutralize its emissions by or round 2050, although local weather advocates known as the plan “imprecise.”